Medically reviewed by Kate Hilton RD
On 19 April June 2024
Our gut health is at the forefront of our overall health and well-being. It affects everything from digestive function, immunity, mental health, and our risk of developing chronic diseases.
Identifying the signs and symptoms of an unhealthy gut in its early stage and knowing how to implement different strategies to correct it can significantly improve your health in both the short and long-term.
Why is our gut health important?
You have heard the saying of our brain being the body’s computer, or command centre that controls all the body’s functions, but did you know that the gut is often called the body’s ‘second brain’?
The gut consists of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and plays a critical role in many bodily functions. It aids in digestion, helps absorb nutrients, and helps to fight against harmful pathogens. It is linked to the immune system, mood regulation, and the prevention of chronic and autoimmune diseases cardiovascular disease, arthritis, obesity, and diabetes.
Out gut health helps our body with:
- Digesting food and absorbing nutrients
- Synthesizing important vitamins and minerals
- Protecting against harmful pathogens
- Supporting immune system
- Protect against many chronic diseases
- Regulating metabolism
- Influencing mood and behaviour
- Improving the quality of our sleep
Maintaining a balanced and diverse gut microbiome is essential for good health. Want to learn more about the gut microbiome? Our guide covers everything you need to know including what it is and why it is essential to our overall health.
How do I know if my gut is unhealthy?
An unhealthy gut will usually present a variety of symptoms, common signs of an unhealthy gut include:
- Digestive issues: Persistent bloating, gas, diarrhoea, constipation, or heartburn.
- Food intolerance: You may experience digestive symptoms after consuming certain foods that previously presented no issues.
- Increase in illness: Poor gut health can weaken your immune system.
- Chronic fatigue: Feeling tired all the time can be linked to poor nutrient absorption or even an intolerance to certain foods.
Alternatively, a gut microbiome test can provide you with an overall picture of the health of your gut by measuring gut bacteria diversity and assessing the impact your microbiome has on your overall health.
What affects gut health?
Several factors can impact the health of your gut microbiome:
- Diet: Diets high in sugars and processed foods can accommodate the growth of harmful bacteria. A lack of fibre intake and other compounds found within food (such as resistant starches and other prebiotics) also fails to support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Antibiotics and Certain Medicines: Although medicines are often necessary, antibiotics are unable to differentiate between harmful and beneficial bacteria, often destroying both. This reduction in diversity can lead to gut dysbiosis. Other types of medications include NSAID's such as Naproxen which can damage the lining of the stomach.
- Infections and Illnesses: gastrointestinal infections such as gastroenteritis can damage the lining of the gut, disrupting the balance of gut bacteria and can lead to long term gut health issues such as IBS (irritable bowel syndrome).
- Stress: Chronic stress increases the production of the stress hormone cortisol which can impact gut motility and reduce blood flow to the digestive system. Not only can this cause several digestive symptoms, but it can also lead to an imbalance of gut bacteria.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can damage the lining of the gut and allow bacteria and toxins to enter the bloodstream, this is called leaky gut.
- Sleep Habits: Our body loves having a routine; irregular sleeping patterns, or poor-quality sleep can impact the body's regulatory mechanisms and impact our immune system and natural function of the gut. It can also alter the circadian rhythm of our gut bacteria
- Hydration: Water is crucial for every organ and function in our body. Insufficient hydration can lead to constipation by causing harder, drier stools that are harder to pass.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can speed up the rate at which food passes through our intestines, increases gut motility and encourages diversity in the microbiome. A lack of exercise can lead to slower digestion and cause an imbalance of gut bacteria.
How can I improve my gut health?
Your gut is mostly impacted by diet and lifestyle, improving the state and health of your gut requires several changes to your daily dietary and lifestyle habits.
Foods to improve your gut health
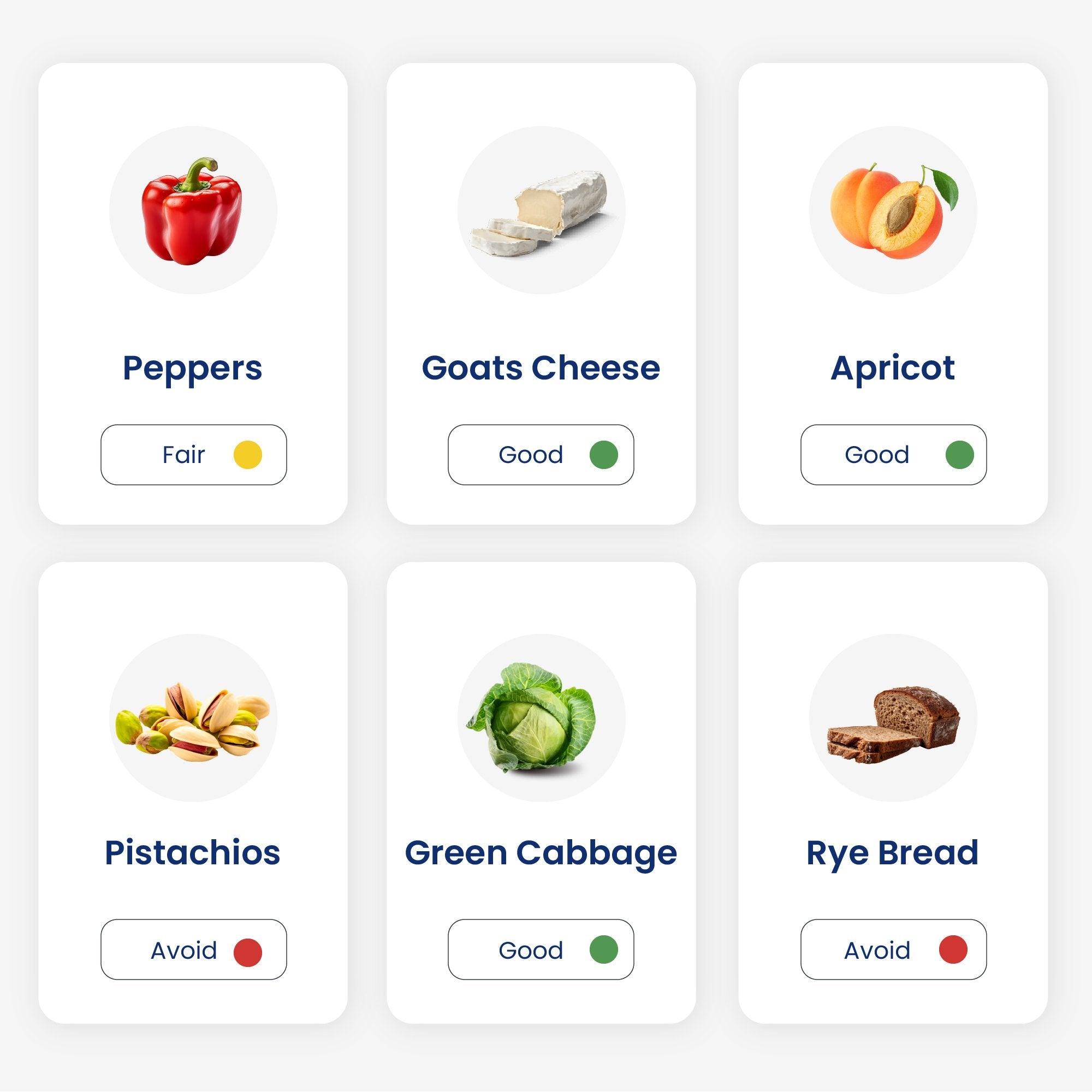
- Fibre-rich foods: The beneficial bacteria in our gut help to ferment fibre into short chain fatty acids (SCFA’s) that are essential to our gut health. Fibre rich foods include fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Probiotics: Foods containing probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria into our gut which helps with the overall bacteria diversity in our microbiome. Yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are all rich in probiotics. Probiotic supplements can also be taken, and these may be more likely to reach the gut alive than probiotic rich foods.
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are foods that contain fibre and other compounds that help to nourish the bacteria in our gut. Foods such as garlic, onion, banana, and oats all contain prebiotics.
If you are looking to adopt probiotics and prebiotics into your diet, find out how you can take them, when you should take them and how they could benefit your gut and overall health.
Recommended read - The best foods for gut health and how they help.
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise: Physical exercise helps us to maintain a healthy bodyweight, encourages regular bowel movements and can speed up the rate that food passes through our intestines.
- Adequate sleep: Ensuring 7-9 hours sleep every night will help to support the body’s natural rhythms. Just as you feel tired after a bad night's sleep, your gut microbes will also feel sluggish and will be working at a reduced capacity.
- Stress management: Managing your stress levels can reduce the production of stress hormones such as cortisol which can impact gut function
- Avoid smoking: It is no surprise that smoking is bad for our gut microbiome as it’s bad for our overall health in every way.
- Hydration: Ensuring consistent water intake throughout the day will keep you hydrated and soften your stools, which helps them pass more easily.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine: Reducing intake of both can protect the gut lining and reduce your risk of leaky gut.
- Mindful eating: Eating slowly can improve digestion and absorption of nutrients by ensuring thorough chewing and reducing digestive strain.
How long does it take to improve gut health?
Improving your gut health depends on the status of your gut. For a minor imbalance in good and bad bacteria within the gut, you may see noticeable changes to your symptoms within a few days or weeks after implementing diet and lifestyle changes, and evidence shows our gut microbiome can significantly improve even after a few days of eating a more gut-health friendly diet.
Gut dysbiosis is a more severe imbalance of the bacteria within the gut, that has typically been neglected for some time and can significantly impact your overall health and cause symptoms to worsen. Correcting gut dysbiosis will require making significant changes to your diet and lifestyle and can take weeks to a few months to improve.
Consistency is key to improving your gut health and should be adopted long-term.
How will I know if my gut health has improved?
The main signs that your gut health has improved include:
- Reduced digestive symptoms: Less bloating, regular bowel movements, gas, diarrhoea, or constipation.
- Enhanced mood and energy levels: Improvements in mental health, energy levels and overall wellness.
- Better sleep: Quality and duration of restorative sleep.
- Improved skin health: The gut and the skin are connected via the gut-skin axis, improving gut health can help improve inflammation that may appear on the skin and may even lead to clearer, healthier-looking skin.
Additionally, you can take a gut microbiome test before and after making these changes to visually confirm changes in the composition of your gut bacteria.
What does a healthy microbiome look like?
Our thoughts
Improving your gut health is a journey that involves making sustained dietary and lifestyle changes. By understanding what affects your gut and implementing the recommended strategies, you can enhance not only your digestive health but your overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider before making significant changes, especially if you have existing health conditions.
Additional references